The interactivity capability within InteractivAI improves the speed and accuracy of seismic analysis workflows.
Ana Krueger, Global Technical Advisor & Customer Success Team Manager
Introduction
Unlike many deep learning (DL) solutions that rely heavily on pre-trained models, InteractivAI thrives on the active involvement of experts, making it the only deep learning tool capable of truly capturing and leveraging the interpreter’s knowledge. This innovative approach ensures robust and relevant results by placing the geoscientist at the center of the machine learning process.
Real-Time Feedback and Refinements
Geoscientists play a pivotal role in guiding the network as it trains, shaping predictions, and ensuring that the results align with both expertise and experience when using InteractivAI. The unique feature that makes these networks interactive is the establishment of a real-time feedback loop, which allows users to make immediate adjustments and refinements to the network training data, fostering an active role in the interpretation process. Unlike pre-trained networks that offer limited flexibility, InteractivAI collaborates with geoscientists to understand and refine interpretations dynamically.
One of the tool’s most impressive capabilities is its learning efficiency. On average, users label just 1% of their data and the network generates 3D predictions across the entire dataset within 30 to 45 seconds. This speed of interactivity accelerates mapping workflows, allowing teams to focus on high-value tasks rather than repetitive labeling.
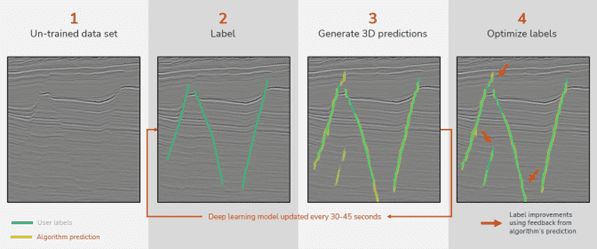
The Role of Interactivity in Speed and Scenario Creation
InteractivAI empowers teams to generate and iterate through multiple scenarios more rapidly than ever before. Moreover, interactivity introduces the opportunity for interpreter bias to play a constructive role. Bias, often seen as a challenge in data interpretation, can be leveraged in InteractivAI to develop comprehensive interpretations that account for various perspectives.
For instance, a Bluware client recently employed a team-driven approach to fault network interpretation. Several geoscientists analyzed the same dataset, resulting in multiple case scenarios that were similar yet varied due to individual perspectives. By combining these insights, the team created one comprehensive interpretation—a process that highlighted the power of interactivity and collaboration.
The project underscored the importance of bias and differing perspectives in achieving more accurate results. By leveraging the knowledge of interpreters with experience in different regions, the team was able to refine interpretations and elevate the overall quality of their findings. This process created a unique opportunity for knowledge transfer within teams. Furthermore, by streamlining workflows and minimizing repetitive tasks, InteractivAI enabled the geoscientists to focus their efforts on high-value analysis, fostering innovation and efficiency in seismic data interpretation.
Conclusion
The power of interactivity within InteractivAI opens new frontiers into what’s possible in seismic workflows. By placing geoscientists at the core of the machine learning process, this tool bridges the gap between human expertise and AI efficiency. From faster scenario creation to real-time feedback, InteractivAI empowers teams to achieve higher confidence and greater accuracy in their interpretations. As the industry continues to evolve, tools like InteractivAI are setting new standards for collaboration, innovation, and precision.
